Knowledge base
tips & tricks
- Set system time automatically on Linux
- Linux Tips and Tricks
- Set system time automatically
- Set correct Timezone
- Flush DNS Cache Unbuntu
- Start / Stop /Restart BIND DNS Server
- Hardening of Linux
- Tutorial on ufw
- Fix Error fwupd-refresh
- Enable ssh login with a public key
- Mount SAMBA shares
- Check for open ports
- Network browsing not working
- Display IP address on Panel in Xfce
- Biometrics: Fingerprint
- Disable SELinux on Fedora
- Create boot USB
- Install PVE-VDIClient on Arch Linux
- Install network scanner on Archlinux
- Install xrdp
- Install Cockpit and Firewalld on Debian 12
- Install xrdp on Fedora 42
- Install send mail service on Fedora
- Install sendmail service on Debian
- Install xrdp on Fedora Xfce
- 10 GbE Network Tuning on Fedora
- 10 GbE Network Tuning on Debian
- Autoupdate on Debian
- Add a user to the sudoers group on Debian 13
- Add E-Mail account to MS Outlook
- Add M365 account to Apple Mail
- MacOS Tips & Tricks
- How to Disable SIP
- Boot into recovery mode
- MacOS - Flush DNS Cache
- MacOS - Privacy hint / OCSP patch
- Map a shared drive on MacOS
- Speedup Settings for 10 GbE
- Proxmox Virtual Environment - PVE
- Import the voyager Root Certificate into your system
- Add custom certificates to Apache
- Add metager as search engine to your browser
- Thunderbird
- CSA Webflow
- Manual installation of WinBox
- Vivaldi - HSTS problem
- Docker Tips & Tricks
Set system time automatically on Linux
Introduction
It is possibly to set and synchronize the time in Linux automatically through the systemd service. It's the successor of NTP daemon. In my network the mt-engine01.simmy.ch provides system time. Hence the device can change, I created an DNS alias ntp.simmy.ch. Using this alias allows changes of the time source without problems.
Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
nano /etc/systemd/timesyncd.confThis file is part of systemd.
#
# systemd is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the
# terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
# Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option)
# any later version.
#
# Entries in this file show the compile time defaults. Local configuration
# should be created by either modifying this file, or by creating "drop-ins" in
# the timesyncd.conf.d/ subdirectory. The latter is generally recommended.
# Defaults can be restored by simply deleting this file and all drop-ins.
#
# See timesyncd.conf(5) for details.
[Time]
NTP=ntp.simmy.ch
FallbackNTP=0.pool.ntp.org, 1.pool.ntp.org, 2.pool.ntp.org
#RootDistanceMaxSec=5
#PollIntervalMinSec=32
#PollIntervalMaxSec=2048systemctl restart systemd-timesyncdDebian
apt install systemd-timesyncd
nano /etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf# This file is part of systemd.
#
# systemd is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the
# terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
# Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option)
# any later version.
#
# Entries in this file show the compile time defaults. Local configuration
# should be created by either modifying this file, or by creating "drop-ins" in
# the timesyncd.conf.d/ subdirectory. The latter is generally recommended.
# Defaults can be restored by simply deleting this file and all drop-ins.
#
# See timesyncd.conf(5) for details.
[Time]
NTP=ntp.simmy.ch
FallbackNTP=0.pool.ntp.org, 1.pool.ntp.org, 2.pool.ntp.org
#RootDistanceMaxSec=5
#PollIntervalMinSec=32
#PollIntervalMaxSec=2048
systemctl restart systemd-timesyncdSet the correct timezone
Figure out the timezone:
timedatectl list-timezones | grep EuropeSet the timezone
timedatectl set-timezone Europe/ZurichUseful commands / checks
root@iVentoy ~# timedatectl status
Local time: Sat 2024-01-06 16:21:29 CET
Universal time: Sat 2024-01-06 15:21:29 UTC
RTC time: Sat 2024-01-06 15:21:29
Time zone: Europe/Zurich (CET, +0100)
System clock synchronized: yes
NTP service: active
RTC in local TZ: no
root@iVentoy ~#root@iVentoy ~# systemctl status systemd-timesyncd
* systemd-timesyncd.service - Network Time Synchronization
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/systemd-timesyncd.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2024-01-06 15:51:09 CET; 31min ago
Docs: man:systemd-timesyncd.service(8)
Main PID: 3022 (systemd-timesyn)
Status: "Contacted time server 46.140.15.108:123 (0.debian.pool.ntp.org)."
Tasks: 2 (limit: 4650)
Memory: 1.3M
CPU: 39ms
CGroup: /system.slice/systemd-timesyncd.service
`-3022 /lib/systemd/systemd-timesyncd
Jan 06 15:51:09 iVentoy systemd[1]: Starting systemd-timesyncd.service - Network Time Synchronization...
Jan 06 15:51:09 iVentoy systemd[1]: Started systemd-timesyncd.service - Network Time Synchronization.
Jan 06 15:51:09 iVentoy systemd-timesyncd[3022]: Contacted time server 46.140.15.108:123 (0.debian.pool.ntp.org).
Jan 06 15:51:09 iVentoy systemd-timesyncd[3022]: Initial clock synchronization to Sat 2024-01-06 14:51:09.538088 UTC.
root@iVentoy ~#date
Useful links
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-set-up-time-synchronization-on-debian-10
Linux Tips and Tricks
Set system time automatically
Introduction
It is possibly to set and synchronize the time in Linux automatically through the systemd service. It's the successor of NTP daemon. In my network the mt-engine01.simmy.ch provides system time. Hence the device can change, I created an DNS alias ntp.simmy.ch. Using this alias allows changes of the time source without problems.
Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
nano /etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf
# This file is part of systemd.
#
# systemd is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the
# terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
# Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option)
# any later version.
#
# Entries in this file show the compile time defaults. Local configuration
# should be created by either modifying this file, or by creating "drop-ins" in
# the timesyncd.conf.d/ subdirectory. The latter is generally recommended.
# Defaults can be restored by simply deleting this file and all drop-ins.
#
# See timesyncd.conf(5) for details.
[Time]
NTP=ntp.simmy.ch
FallbackNTP=0.pool.ntp.org, 1.pool.ntp.org, 2.pool.ntp.org
#RootDistanceMaxSec=5
#PollIntervalMinSec=32
#PollIntervalMaxSec=2048systemctl restart systemd-timesyncd
timedatectl timesync-status
Server: 192.168.1.74 (192.168.1.74)
Poll interval: 1min 4s (min: 32s; max 34min 8s)
Leap: normal
Version: 4
Stratum: 3
Reference: 2E8C0F6C
Precision: 1us (-24)
Root distance: 76.324ms (max: 5s)
Offset: +1.117ms
Delay: 326us
Jitter: 0
Packet count: 1
Frequency: -25.696ppmDebian 10
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-set-up-time-synchronization-on-debian-10
apt purge ntp
apt install systemd-timesyncd
nano /etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf# This file is part of systemd.
#
# systemd is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the
# terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
# Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option)
# any later version.
#
# Entries in this file show the compile time defaults. Local configuration
# should be created by either modifying this file, or by creating "drop-ins" in
# the timesyncd.conf.d/ subdirectory. The latter is generally recommended.
# Defaults can be restored by simply deleting this file and all drop-ins.
#
# See timesyncd.conf(5) for details.
[Time]
NTP=ntp.simmy.ch
FallbackNTP=0.pool.ntp.org, 1.pool.ntp.org, 2.pool.ntp.org
#RootDistanceMaxSec=5
#PollIntervalMinSec=32
#PollIntervalMaxSec=2048systemctl start systemd-timesyncd
systemctl status systemd-timesyncd
date
Set correct Timezone
Howto set the correct timezone in Linux Ubuntu
Get all possible timezones:
timedatectl list-timezonesSet the local timezine:
timedatectl set-timezone Europe/ZurichCheck the local timezone:
timedatectlHowto set the correct timezone in Debian 10
dpkg-reconfigure tzdataUseful links
https://linuxize.com/post/how-to-set-or-change-timezone-on-ubuntu-20-04/
Flush DNS Cache Unbuntu
Introduction
Ubuntu caches DNS queries local. As long as the DNS address of a node does not change, this is very useful. Unless there is a change and the client should react very quickly, you have to flush/delete to cache. This manual describes hot to do that.
Method I: Flush the cache
Take a look at the cache:
resolvectl statisticsClear the cache:
resolvectl flush-cachesMethod II: Flush the cache
systemd-resolve --flush-caches
systemd-resolve --statisticsMethod III: Flush the cache
killall -USR2 systemd-resolvedStart / Stop /Restart BIND DNS Server
Introduction
For testing purposes I am using Univention with bind9. The greater goal is to use AD/SAMBA from Univention. After testing for a couple of weeks suddenly some DNS addresses do not get resolved. The same problems occurred on Zentyal.
So far I couldn't find a reason for this misbehavior. However, a restart of the bind9 service seems to patch the problem.
Debian based Linux
Start the service
service bind9 startStop the service
service bind9 stopRestart the service
service bind9 restartReload the service
This will become necessary of a configuration file is changed.
service bind9 reloadCheck status
service bind9 statusFedora based Linux
Start the service
systemctl start namedStop the service
systemctl stop namedRestart the service
systemctl restart namedCheck status
systemctl status namedHardening of Linux
Introduction
Despite the fact that Linux is Open Source and Linux it comes as a surprise that in the default installation are some hidden trackers and spy software.
Hardening
There is a script that will remove all malware. Originally written for Linux, but it can easily adopted for other distributions.
This script does:
- System update and software upgrade
- Amazon & advert web apps removing
- AptUrl Removing ( tool, which gives possibilities to start installation by clicking on url, can be executed with js, which is not secure)
- Guest session disable for LightDM
- Remote login disable for LightDm
- DNS encryption (dnscrypt-proxy)
I don't recommend this, hence my DNS server is not working with encryption.
apt -y remove dnscrypt-proxy - FireWall (UFW)
- Antivirus (ClamAV)
- Brute Force protection (Fail2Ban)
- Basic Telemetry Removing (ZeitGeist) and unsecure libs and pre-installed software with high and potentional risks
Here is a version for rpm based systems:
#!/bin/bash
# This script removes telemetry and enhances system security on an RPM-based Linux distribution.
# System Up to Date:
sudo dnf -y update
sudo dnf -y upgrade
# ========
# Remove any pre-installed telemetry or unwanted software (no direct equivalents for `unity-lens-shopping` and `unity-webapps-common` on RPM-based systems):
# Remove pre-installed software that may be tracking or unwanted:
sudo dnf -y remove gnome-online-accounts
sudo dnf -y remove gnome-shell-extension-prefs
sudo dnf -y remove gnome-software
# ========
# Disable Guest session & remote login for LightDM (if LightDM is in use):
if [ -f /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf.d/50-no-guest.conf ]; then
sudo sh -c 'printf "[Seat:*]\nallow-guest=false\ngreeter-show-remote-login=false\n" > /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf.d/50-no-guest.conf'
sudo dnf -y remove lightdm-remote-session-freerdp
sudo dnf -y remove lightdm-remote-session-uccsconfigure
fi
# ========
# Remove any equivalent telemetry-related packages:
# Note: zeitgeist is generally specific to Ubuntu/Debian, so we focus on similar tools on RPM systems.
# Remove `tracker`, a GNOME-based file indexing and search tool that collects metadata:
sudo dnf -y remove tracker
sudo dnf -y remove tracker-miners
sudo dnf -y remove tracker3
sudo dnf -y remove tracker3-miners
# Remove `gnome-usage`, a system resource monitor that could collect usage data:
sudo dnf -y remove gnome-usage
# Remove `PackageKit`, which can send data back to package servers:
sudo dnf -y remove PackageKit
# ========
# DNS encryption:
sudo dnf -y install dnscrypt-proxy
# ========
# FireWall (using firewalld):
sudo dnf -y install firewalld
sudo systemctl start firewalld
sudo systemctl enable firewalld
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --set-default-zone=block
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
# ========
# ClamAV Antivirus Installation:
sudo dnf -y install clamav
sudo dnf -y install clamav-daemon
sudo systemctl enable clamav-daemon
sudo systemctl start clamav-daemon
# ========
# Fail2Ban installation (protects from brute force login):
sudo dnf -y install fail2ban
sudo systemctl enable fail2ban
sudo systemctl start fail2ban
# ========
# Remove other potentially problematic or unused packages:
# Removing `cups` if you don't need printer support:
# sudo dnf -y remove cups
# Remove `remmina` if you don't use it for remote connections:
# sudo dnf -y remove remmina
# Remove unnecessary GNOME components:
sudo dnf -y remove evolution
sudo dnf -y remove evolution-data-server
sudo dnf -y remove gvfs-fuse
sudo dnf -y remove vino # VNC server (remote desktop sharing)
sudo dnf -y remove gnome-shell-extension-background-logo # Fedora logo on desktop background
sudo dnf -y remove gnome-user-share # Potentially shares user data over the network
sudo dnf -y remove libreport-plugin-bugzilla # Automatic bug reporting to Bugzilla
sudo dnf -y remove abrt-addon-xorg # Automatic bug reporting for Xorg
sudo dnf -y remove abrt-cli # Command-line tool for automatic bug reporting
sudo dnf -y remove abrt-addon-ccpp # Automatic bug reporting for C/C++ programs
sudo dnf -y remove abrt-addon-kerneloops # Automatic bug reporting for kernel oopses
sudo dnf -y remove abrt-addon-pstoreoops # Automatic bug reporting for pstore oopses
# ========
# Autoremove unnecessary dependencies:
sudo dnf -y autoremove
# ========
# Troubleshooting:
# If the internet does not work, try restarting dnscrypt-proxy:
# sudo systemctl restart dnscrypt-proxy
# Also, the tool may use another port, detect the port in this output:
# sudo ss -ntulp
# Then add the port to firewalld:
# sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=[portnumber]/tcp
# sudo firewall-cmd --reload
# ========
Tutorial on ufw
UFW, or Uncomplicated Firewall, is a simplified firewall management interface that hides the complexity of lower-level packet filtering technologies such as iptables and nftables. If you’re looking to get started securing your network, and you’re not sure which tool to use, UFW may be the right choice for you.
Here is a link that shows how to set up the firewall on Ubuntu:
How To Set Up a Firewall with UFW on Ubuntu 22.04
Fix Error fwupd-refresh
Introduction
After installing monitoring (check_mk) I realized that the servis fwupd-refresh produces a critical error. However, this is based on a configuration mishap in the service itself. Here is the fix.
The service is able to perform a firmware update on UEFI machines. The service is totally useless on VMs.
Correction Step-by-Step
Edit file /lib/systemd/system/fwupd-refresh.service
Replace SuccessExitStatus=2 with SuccessExitStatus=1
Restart the service:
systemctl daemon-reload && sudo systemctl start fwupd-refresh.service
Check the service
systemctl status fwupd-refresh.service
Disable the service
Another possibility is to disable the service:
systemctl disable fwupdUseful links
https://askubuntu.com/questions/1404691/fwupd-refresh-service-failed
https://askubuntu.com/questions/1227508/consequences-of-disabling-fwupd
Enable ssh login with a public key
Introduction
it is more secure and easier to login to a server over ssh if you place your public key on this server. This how-to shows in simple steps how to do this.
Generate keys
You only have to do this one time. You can and should reuse your public key for all ssh-servers.
Step 1 - creating SSH key pair
Make sure you are in your home directory.
ssh-keygen -t rsaStep 2 - Copying the SSH public key to the ssh server
The real magic happens here:
ssh-copy-id <username>@<ssh-server>Connect to the server
ssh <username>@<ssh-server>Useful links
https://www.linuxshelltips.com/passwordless-ssh-login/
Mount SAMBA shares
Introduction
There a several ways of mounting SAMBA shares on a Linux machine. This manual gives an overview.
Prerequisite
It makes things easier if the Linux client is a member of an Active Directory domain. Hence I use Zorin OS, this can easily be achieved with the correct setting during the installation:
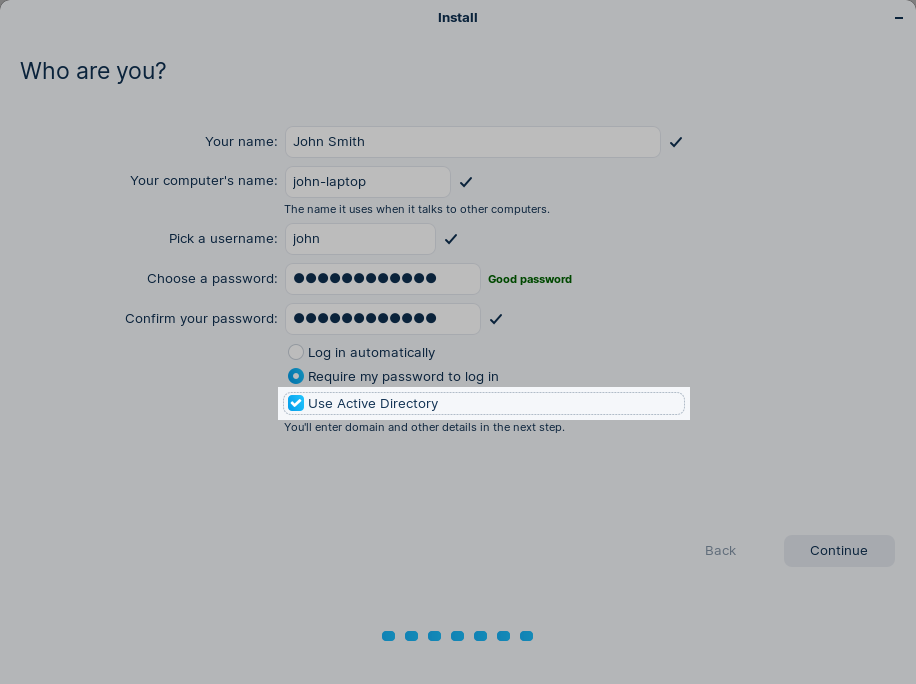
If you want to join a Linux computer to an Active directory, please refer to:
Mount SAMBA shares
Manual mount
mount -t cifs -o username=<user>,password=<secret-password> //xigma-prime.simmy.ch/backup /mnt/backupPermanent mount with fstab
In the fstab, I use the following command:
//xigma-prime.simmy.ch/images /mnt/images cifs credentials=/root/.smbcredentials,uid=1000,forceuid,gid=1000,forcegid 0 0This will mount the share images to the mountpoint /mnt/images. The credentials are saved in the file .smbcredentials:
username=<username>
password=<password in cleartext>
domain=simmy.chPermanent mount with pam_mount
It is more desirable to mount the SAMBA shares when the user logs in, rather during boot.
Installation of the necessary modules
apt install -y libpam-mount keyutils cifs-utils smbclientConfiguration entry in /etc/security/pam_mount.conf.xml
The following lines have to be added to the file after the line <mkmountpoint enable="1" remove="true" />:
<volume
fstype="cifs"
server="xigma-prime.simmy.ch"
path="images"
mountpoint="~/mnt/images"
options="sec=krb5,cruid=%(USERUID),workgroup=SIMMY,vers=3.0" />Permanent mount with GPO
It is possible to utilize GPOs to mount SAMBA shares on a Linux machine, that is joined to an Active Directory. However, I did not try this possibility.
Temporary mount
It is possible to mount a share with a file manager. This mount will be lost after log off or a reboot.
Useful resources
Check for open ports
https://phoenixnap.com/kb/linux-check-open-ports
lsof -nP -iTCP -sTCP:LISTEN
netstat -tunpl
ss -tunlp
nc -z -v localhost 1-65535 2>&1 | grep succeededNetwork browsing not working
Sometimes network browsing or the mapping of a SMB share with a file manager in Linux is not working. I found one of the most likely causes for this problem is a missing package.
After installing gvfs-smb network browsing was working fine.
Installation on Fedora
sudo dnf install gvfs-smb
Display IP address on Panel in Xfce
Create a small shell script show_ip.sh :
#!/bin/bash
# Get all addresses from hostname -I
IP_ADDRESSES=$(hostname -I)
# Split into individual IP addresses
IFS=' ' read -r -a IP_ADDRS <<< "$IP_ADDRESSES"
# Find the first IPv4 address
for IP in "${IP_ADDRS[@]}"; do
if [[ "$IP" =~ ^[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}$ ]]; then
echo "$IP"
break
fi
done
#!/bin/bash
ip -4 addr show scope global | grep -oP '(?<=inet\s)\d+(\.\d+){3}'
chmod +x show_ip.shAdd a generic monitor:
That's it.
Biometrics: Fingerprint
Introduction
Enabling fingerprint login is quite simple on Fedora, hence all necessary software is installed and all configurations are pre-configured.
Configuration
To add a signature for a finger, run:
fprintd-enroll
To verify the newly created fingerprint, use:
fprintd-verify
By default every user is allowed to enroll new fingerprints without prompting for the password or the fingerprint.
Useful links
How to enable fingerprint login?
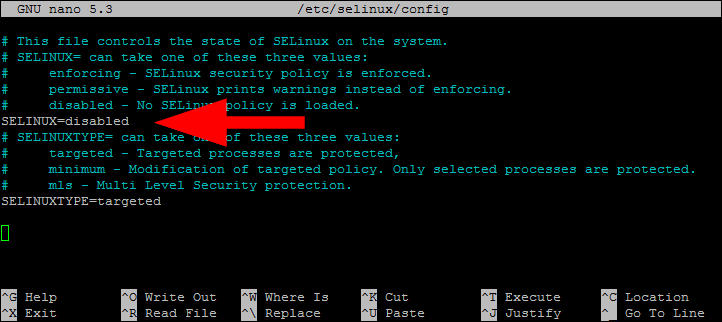
Disable SELinux on Fedora
Permanently Disable SELinux on Fedora
Update the SELinux configuration file and set SELINUX=disabled to permanently disable the SELinux on your system. This will completely disable all the SELinux contexts.
sudo nano /etc/selinux/config
Set SELINUX value to disabled:
SELINUX=disabled
Reboot your instance after making changes.
Note – You can again activate the SELinux by setting SELINUX=enforcing in configuration file.
How to Disable SELinux on Fedora
Create boot USB
Linux
sudo lsblk
sudo dd if=./Fedora-KDE-Live-x86_64-41-1.4.iso of=/dev/sdb bs=4M status=progress oflag=syncMacOS
diskutil list
diskutil unmountDisk /dev/disk5
sudo dd if=./Fedora-KDE-Live-x86_64-41-1.4.iso of=/dev/rdisk5 bs=4M status=progress oflag=sync
diskutil unmountDisk /dev/disk5Install PVE-VDIClient on Arch Linux
Introduction
This VDI client connects directly to Proxmox VE and allows users to connect (via Spice) to any VMs they have permission to access.
Installation
Install this first:
python3-pip python3-tk virt-viewer git
sudo pacman -S python tk virt-viewer git
git clone https://github.com/joshpatten/PVE-VDIClient.git
cd ./PVE-VDIClient/
chmod +x requirements.sh
./requirements.sh
sudo cp vdiclient.py /usr/local/bin
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/vdiclient.py
cp vdiicon.ico ~/icons/
Configuration
On the client
~/.config/VDIClient/vdiclient.ini
[General]
# This is the title that is diplayed to the user
title = VDI Login
# This is the PySimpleGui Theme that is used. Run vdiclient.py with flag `--list_themes` for a list of themes
theme = LightBlue
# Program Icon
icon = vdiicon.ico
# Logo displayed on all windows
logo = vdiclient.png
# Enable Kiosk mode, which does not allow the user to close anything
kiosk = False
# Enable/Disable Fullscreen mode (not applicable in Kiosk mode)
fullscreen = False
# Disable viewer_kiosk mode if kiosk is set to true, this allows overriding remote_viewer kiosk mode
#viewer_kiosk = False
# Enable displaying SPICE ini file before opening virt-viewer
inidebug = False
# Select which guest types to display. Acceptable values: both, lxc, qemu
guest_type = both
# Show VM option for resetting VM
#show_reset = True
# Set Window Dimensions. Only use if window isn't sizing properly
#window_width = 800
#window_height = 600
# PVE-VDIClient supports multiple clusters. Define them with sections that start with Hosts. followed by the name
# you wish to display to your end users. This example is Hosts.PVE which would display PVE to your users
[Hosts.PVE]
# JSON dictionary of servers in the cluster
# Format is 'IP/FQDN': PORT
# NOTE: MAKE SURE THAT ALL LINES ARE INDENTED
hostpool = {
"pve01.simmy.ch" : 8006,
"pve02.simmy.ch" : 8006
}
# This is the authentication backend that will be used to authenticate
auth_backend = pve
# If enabled, 2FA TOTP entry dialog will show
auth_totp = false
# If disabled, TLS certificate will not be checked
tls_verify = false
# User name (if using token)
# NOTE: If only one cluster is defined, this will auto-login
# If user, token_name, and token_value are set
#user = user
# API Token Name
#token_name = dvi
# API Token Value
#token_value = xxx-x-x-x-xxx
# Password Reset Command Launch. Has to be full executable Command
#pwresetcmd = start chrome --app=http://pwreset.example.com
# Automatically connect to a VMID upon authentication
#auto_vmid = 100
# An additional cluster definition
#[Hosts.PVE2]
# JSON dictionary of servers in the cluster
# Format is 'IP/FQDN': PORT
#hostpool = {
# "10.10.10.100" : 8006,
# "10.10.10.111" : 8006,
# "pve1.example.com" : 8006
# }
# This is the authentication backend that will be used to authenticate
#auth_backend = pve
# If enabled, 2FA TOTP entry dialog will show
#auth_totp = false
# If disabled, TLS certificate will not be checked
#tls_verify = false
# User name (if using token)
# NOTE: If only one cluster is defined, this will auto-login
#user = user
# API Token Name
#token_name = dvi
# API Token Value
#token_value = xxx-x-x-x-xxx
# Password Reset Command Launch. Has to be full executable Command
#pwresetcmd = start chrome --app=http://pwreset.example.com
# Automatically connect to a VMID upon authentication
#auto_vmid = 100
[SpiceProxyRedirect]
# The Spice Proxy provided by the Proxmox API may need to have its host/port rewritten
# These rewrite rules are written `IP:port = IP:port`
# 1. Use the inidebug and read the current proxy=pve1.example.com:3128
# 2. Add your proxmox ip to the right side e.g. 123.123.123.123:6000
pve1.example.com:3128 = 192.168.1.99:6000
#[AdditionalParameters]
# If you wish to define additional parameters to pass to virt-viewer you may define them here
# More parameter definitions here: https://www.mankier.com/1/remote-viewer
# Some Examples:
# Enable USB passthrough
#enable-usbredir = true
# Enable auto USB device sharing
#enable-usb-autoshare = trueOn the Proxmox VE server
- Create a user (e.g. pvi) in the realm Proxmox VE authentication server
- Create a group (e.g. Spice Access)
- Add the group to permissions of all SPICE enabled virtual machines
- Add the role PVEVMUser
Licensing
In case there is a warning about Licensing or trial period, you can enter your license key into this file:
~/.config/PySimpleGUI/settings/_PySimpleGUI_settings_global_.json
{"-temp2-": 31082748, "-LICENSE KEY-": "egyhJ1MnawWiNflobjnzN7lSVpHQlbwwZGSvIi6FIjkxR3l9dnmhVpsybz3JBKlgcMibIeslIJkSxmpPYb2BVVuMcV22V6JVRrCsIc6QMITNciyMNpDRQrzyMXzGAVwnOsCPwUi8TyG9lfj7ZPWU5qzuZpUSRllOcdGvx9vneDW21MlyblnkRXWOZgXDJUzgaNWA9Nu2IJjcoSxKLiCIJpObYAWE12laRumblByOck3ZQYiFOQisJdIrbc2bxMn6ZsXWI6iULRC4JDOhY6Wu1IlmThGvFmzWdiCXI36WI7l4N1jcazG8luupZbG8xKlKcOiOIQsmIrkKNYvRbAXtBPh5bSn3kHi6Oli3IfiULOCFJwDddVXoNT0PbQ2b1Yl2c2kBlDERIfj9oliZM8zkUj1YOQDuMeiNLPCgJPEJYnXNRulESeX6NtzcdKWkVgkMIrjvoYigMWDEgxvnMKjrMHvnM2jqAsyWNDCtIoskIhkYRFh3dLGNVzFAetHSBVpvcam6VkzbIgjQofiGMFDPg3vPMmjpMOvnMgjWA5yQNGSKIrsjIxktVOt8YHW6lqsvQnWyRHkCcSmdV1zIcZyYI56LIYmmgGuSc62AN4o3axWM5mkTbPGOVpy7QGH4BvyObp3iR9vxbOmZ1LhwaIWHwsuDYE2egEi8LmC9JoJEU4EDF0k8ZNHjJLlUcy39MdizOHiSI44TN5S04SxjODTDUMurMEjBIw5HLvjZQhyeIpnN0u=9733ae7aa77212d35ae97ed325e69a9c0312af879bbac5a6c389d1873619b5313d3d32322e397b013ac43265bdb0d19b7df45c9157a6d7552fb5591b6aef5d42ef48fd5424265a1e0e849562dbdecd12dfd6c7cbb06fd9e1a7dbc51e63716e69c978ca072cc2a331c2cb052198431513cfa57e240d98e6cb0aa665ad0ec7db0ff287cd411666fa5134e064b34611674246dc4a3db98c8b3501a388f3812e4c63adf046a9eab973b76077bbb67bd874499f59f5801b37b795ab9cdf0d87b549cd02cbc6794ad2a3a71ad3f9833c76fa0e760b0f950c7e06a9d4beb299d22c41f33cf346af4c9219de9ea396268f67a6adc22ac97931a742841b591f63e816bf9891205e18d4ad8dedf1e7b43c76bab43ac99e77e28476746b1400d6b6ea06c9c26464b922f858c3ff0b9a9b4bbb49831cd7db5729570d05e1ffcc6fb8635108d60337c74ad81154b003d567b7a8fb5d098d0296e3ab9925f71c442676c697930856642d68a4132d4156226466402f057637933319b1906df45679665d18cfbdcf06a6bb4b9188134f18a71e9605fc4697bd5de6340f824693e18de579155294b7e4606b305c90cbfd82bb9298a9b01237deee29bb3a0c51cd20e0ba4622954724165a36a2f3fe9ea1c4c64f90c6c5ba6e2cbdbcbff782a0e63c758e58f0d300274a9c4b6d5384b31968e294f4117ce898864c622245a50d0772882cedba63aa00f", "-temp1-": "67707579", "-trial period warned-": false}
Useful links
Install network scanner on Archlinux
Install the drivers with pamac
run the commandline:
sudo brsaneconfig4 -a name=Brother model=MFC-9330CDW ip=192.168.1.108check if it is working
scanimage -Ldevice `brother4:net1;dev0' is a Brother Brother MFC-9330CDW
device `v4l:/dev/video2' is a Noname Logitech BRIO virtual device
device `v4l:/dev/video0' is a Noname Logitech BRIO virtual devi
Install xrdp
Introduction
Fedora
sudo dnf install -y xrdp xorgxrdp
sudo systemctl enable xrdp
sudo systemctl start xrdp
sudo systemctl status xrdpCreate the group tsusers and add all users using Remote Desktop to it
Open Firewall on port 3389
Check if the service is listening on tcp4
sudo nano /etc/xrdp/xrdp.ini
port=tcp://:3389
; Some session types such as Xorg and Xvnc start a display server.
; Startup command-line parameters for the display server are configured
; in sesman.ini. See and configure also sesman.ini.
[Xorg]
name=Xorg
lib=libxup.so
username=ask
password=ask
port=-1
code=20
Install Cockpit and Firewalld on Debian 12
Install Cockpit, Firewalld, and Open Ports on Debian 12
1. Update the System
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -y2. Install Cockpit
sudo apt install -y cockpit
sudo apt install cockpit-networkmanager -y
sudo apt install cockpit-doc -y
sudo apt install cockpit-packagekit -y3. Enable and Start Cockpit
sudo systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket4. Install firewalld
sudo apt install -y firewalld
sudo systemctl enable --now firewalld
sudo apt install cockpit-machines cockpit-pcp network-manager cockpit-networkmanager -ysudo apt remove --purge ufw5. Open Required Ports in firewalld
- SSH (port 22): For remote access
- HTTP (port 80): For web traffic
- HTTPS (port 443): For secure web traffic
- Cockpit (port 9090): For Cockpit web UI
- Webmin (port 12321): For Webmin web UI (on Turnkey images, default is port 1000)
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=ssh --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=https --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=cockpit --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=12321/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reload6. Verify firewalld Rules
sudo firewall-cmd --list-all7. Access Cockpit and Webmin
- Cockpit:
https://your-server-ip:9090 - Webmin:
https://your-server-ip:12321
References
- Official Cockpit documentation: cockpit-project.org
- HowtoForge: Install Cockpit Web Console on Debian 12
- edafe.de: Install Cockpit on Debian 12 bookworm
- Webmin Firewall: webmin.com/firewall.html
Install xrdp on Fedora 42
How to Set Up XRDP on Fedora 42 XFCE
Follow these steps for a reliable and quick XRDP setup with XFCE on Fedora 42:
- Install XRDP and XFCE (if not already installed)
sudo dnf install xrdp xorgxrdp
2. Enable and Start XRDP Service
sudo systemctl enable --now xrdp
3. Configure the Firewall
open Port 3389 for rdp
4. Set Up the XFCE Session for XRDP
Create a file named .Xclients in your home directory with the following content:
echo "xfce4-session" > ~/.Xclients
echo "xfce4-session" > ~/.Xclients
chmod +x ~/.Xclients6. Restart XRDP Services
sudo systemctl restart xrdp
sudo systemctl restart xrdp-sesman
7. Connect via RDP
-
Use Devolutions RDM or any RDP client.
-
Enter your Fedora machine's IP address and credentials.
Summary Table
| Step | Command/Action |
|---|---|
| Install XRDP | sudo dnf install xrdp xorgxrdp |
| Enable & start service | sudo systemctl enable --now xrdp |
| Firewall open port | sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3389/tcp; sudo firewall-cmd --reload |
| Configure session | echo "xfce4-session" > ~/.Xclients; chmod +x ~/.Xclients |
| (Optional) SELinux fix | sudo chcon --type=bin_t /usr/sbin/xrdp* |
| Restart XRDP | sudo systemctl restart xrdp xrdp-sesman |
This setup gives you a fast, graphical remote desktop on Fedora XFCE with minimal hassle.
Install send mail service on Fedora
Overview
This guide explains how to set up authenticated email sending from the command line on Fedora using msmtp (a lightweight SMTP client) and s-nail (a mailx-compatible mail utility). This method is ideal for scripts and system notifications in environments where only authenticated SMTP is allowed.
1. Install Required Packages
sudo dnf install -y msmtp s-nail2. Configure msmtp
- Copy the example configuration (optional):
sudo cp /usr/share/doc/msmtp/msmtprc-system.example /etc/msmtprc - Edit
/etc/msmtprcand adjust to your SMTP provider:sudo nano /etc/msmtprcExample configuration:
defaults auth on tls on tls_trust_file /etc/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crt logfile /var/log/msmtp.log account default host mail.hosting.de port 587 from admin@simmy.org user admin@simmy.org password <super-secret> - Set permissions to protect your password:
sudo chmod 600 /etc/msmtprc
3. Configure s-nail to Use msmtp
Add the following line to /etc/s-nail.rc or your ~/.mailrc:
set mta=/usr/bin/msmtp4. Send a Test Email
echo "This is the body" | mail -s "Test Subject" recipient@example.com- If the command returns no errors, the mail was sent successfully.
- Check
/var/log/msmtp.logfor troubleshooting if needed.
5. Notes
- If you receive an error like "Authenticated user is not permitted to override sender address", ensure the
fromaddress in/etc/msmtprcmatches the authenticated SMTP user, or configure your SMTP provider to allow the desired sender address. - For use in scripts (e.g., backup notifications), simply use the
mailcommand as shown above.
References
- Sending e-mails via mailbox.org with msmtp on Fedora
- Fedora Docs: Mail Servers
- Fedora Forum: Sending mail with the (mailx) command
Install sendmail service on Debian
Overview
This guide explains how to set up authenticated email sending from the command line on Debian-based systems (including Proxmox Backup Server) using msmtp (a lightweight SMTP client) and s-nail (a mailx-compatible utility). This is ideal for system notifications, backup/email scripts, and environments with DMARC/SPF filtering where authenticated sending is required.
1. Install Required Packages
apt update
apt install -y msmtp s-nail 2. Configure msmtp
- Create/Edit the global configuration file:
nano /etc/msmtprc - Example
/etc/msmtprc:defaults auth on tls on tls_trust_file /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt logfile /var/log/msmtp.log syslog LOG_MAIL account default host mail.hosting.de port 587 from admin@simmy.org user admin@simmy.org password-
Important: "from" and "user" should match your authenticated email address for DMARC/SPF.
-
-
Example 2 /etc/msmtprc
-
syslog LOG_MAIL defaults auth on tls off tls_trust_file /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt logfile /var/log/msmtp.log account ucs-backup host ucs-backup.simmy.ch port 25 from pbs01@simmy.ch account default : ucs-backup
-
Use only plain ASCII spaces (no tabs or Unicode spaces).
-
- Set strict permissions:
chmod 600 /etc/msmtprc
3. Configure s-nail or mailx to use msmtp
Add the following line to your /etc/s-nail.rc (system-wide) or ~/.mailrc (per user):
set mta=/usr/bin/msmtp4. Send a Test Email
Use the mail command to test sending:
echo "This is the body" | mail -s "Test Subject" recipient@example.com On success, no output is shown. Check /var/log/msmtp.log or /var/log/mail.log (if syslog is enabled) for debug info if not delivered.
5. Troubleshooting
- If mail arrives in Junk/Spam, create a filter at your destination mailbox to whitelist the sender or move to Inbox.
- If you see an error like “account default was already
Install xrdp on Fedora Xfce
Overview
This document describes how to install and configure the XRDP server on Fedora 43 with the Xfce desktop environment so that Windows, macOS, and Guacamole clients can connect via RDP. Each Linux user who should be able to log in via XRDP needs their own startwm.sh to launch Xfce correctly.
Prerequisites
- Fedora 43 VM or physical host with the Xfce desktop environment installed (PRETTY_NAME="Fedora Linux 43 (Xfce)"). [web:14]
- Root or sudo access on the Fedora system.
- Network connectivity from RDP clients (Windows, macOS, Guacamole) to TCP port 3389 on the Fedora host.
Install and Enable XRDP
Install XRDP and its Xorg backend, then enable and start the service. Fedora 40/41 XRDP documentation uses the same pattern and works on Fedora 43. [web:21][web:17]
sudo dnf install -y xrdp xorgxrdp
sudo systemctl enable --now xrdp
sudo systemctl status xrdpOpen the Firewall for RDP
If firewalld is running, open TCP port 3389 permanently and reload the firewall rules. [web:21][web:17]
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3389/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadCreate startwm.sh for Each User
On Fedora, XRDP uses a per-user startup script named startwm.sh in the user's home directory to start the desktop session. Fedora's XRDP guide shows this pattern for multiple desktops; for Xfce the command is dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/startxfce4.
Repeat the following steps for each user account that should be able to log in via XRDP:
# as the target user (not root)
cat > ~/startwm.sh << 'EOF'
#!/bin/sh
export LANG=en_US.UTF-8
export LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8
exec dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/startxfce4
EOF
chmod 755 ~/startwm.sh
Explanation:
dbus-launch --exit-with-sessionensures a proper D-Bus session is created for Xfce, which is required for a fully functional desktop over XRDP./usr/bin/startxfce4starts the Xfce session.chmod 755makes the script executable so XRDP can run it at login.
Optional: Global /etc/xrdp/startwm.sh
If you want a single configuration for all users, you can copy the same script to /etc/xrdp/startwm.sh so XRDP uses it globally. This approach is also referenced in XRDP discussions about custom session commands.
sudo cp /home/<username>/startwm.sh /etc/xrdp/startwm.sh
sudo chmod 755 /etc/xrdp/startwm.sh
sudo systemctl restart xrdp
Replace <username> with a real user name when copying from an existing script.
SELinux Considerations (Optional)
On some Fedora installations, SELinux can interfere with XRDP. Recent XRDP-on-Fedora guides use chcon to assign the bin_t type to XRDP binaries if SELinux denials occur. [web:17]
sudo chcon --type=bin_t /usr/sbin/xrdp
sudo chcon --type=bin_t /usr/sbin/xrdp-sesman
sudo systemctl restart xrdpTesting with a Native RDP Client
Test XRDP with a standard RDP client before integrating with Guacamole. Fedora XRDP documentation uses Windows Remote Desktop as the reference client. [web:21]
- From a Windows machine, open Remote Desktop Connection (
mstsc.exe). - Enter the Fedora host name or IP (for example
fedora-xfce.example.local) and connect. [web:21] - Log in using a Fedora user that has a
~/startwm.shconfigured. - Verify that an Xfce desktop session appears and is usable.
Using XRDP from Guacamole
Once XRDP and Xfce are working locally, Guacamole can connect using the RDP protocol. The key is to match the security mode and certificate options so that negotiation succeeds.
| Setting | Value |
| Protocol | RDP |
| Hostname | IP Address |
| Port | 3389 |
| Username | ${GUAC_USERNAME} |
| Password | ${GUAC_PASSWORD} |
| Security Mode | TLS |
| Ignore server certificate | enable |
Summary
- Install XRDP and Xorg backend with
dnf install -y xrdp xorgxrdp, then enable the service. - Open the firewall for TCP port 3389 if
firewalldis running. - Create a per-user
~/startwm.shcontainingdbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/startxfce4and make it executable. - Optionally, place the same script at
/etc/xrdp/startwm.shfor a global configuration. - Verify RDP access with a native client (e.g., Windows mstsc), then configure an RDP connection in Guacamole pointing at the Fedora 43 XRDP server.
10 GbE Network Tuning on Fedora
mount -t cifs //n2/share /mnt/n2 \
-o vers=3.1.1,sec=ntlmssp,cache=strict,echo_interval=60,actimeo=1,soft \
,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,uid=1000,gid=1000Those options mirror what Red Hat and others recommend for high‑bandwidth SMB on modern kernels.
10 GbE Network Tuning on Debian
Introduction
This document describes a small, focused kernel network tuning for Debian systems connected via 10 GbE, using a custom /etc/sysctl.d/10g.conf file and the standard sysctl mechanism to apply the settings. These values follow common recommendations for high‑bandwidth Linux hosts by increasing TCP buffer limits and using modern congestion control and queuing disciplines.
Purpose of 10g.conf
The goal of 10g.conf is to allow the TCP stack to efficiently fill a 10 Gb/s link for protocols like SMB and NFS while remaining conservative enough for general‑purpose servers. It does this by:
- Increasing the maximum socket buffer sizes for receive and transmit.
- Raising the autotuning ceiling for TCP read and write buffers.
- Improving backlog and connection queue limits for busy hosts.
- Enabling modern congestion control (
htcp) and fair queuing (fq).
10g.conf Content
Create /etc/sysctl.d/10g.conf with the following content:
# /etc/sysctl.d/10g.conf
# Basic 10 GbE TCP tuning for Debian / Linux.
# Focus: higher throughput for SMB/NFS and other bulk transfers over 10G.
# Allow larger TCP socket buffers for high-bandwidth links
net.core.rmem_max = 33554432
net.core.wmem_max = 33554432
net.core.rmem_default = 262144
net.core.wmem_default = 262144
# TCP autotuning limits: min, default, max
net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 87380 33554432
net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 65536 33554432
# Optional but often helpful for busy 10GbE hosts
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 250000
net.core.somaxconn = 4096
# Use modern congestion control and fair queueing
net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control = htcp
net.core.default_qdisc = fqParameter Notes
net.core.rmem_max/wmem_max: Maximum per‑socket buffer size; 32 MB is typical for 10 GbE hosts and is widely recommended.tcp_rmem/tcp_wmem: Trio of values (min, default, max) used by TCP autotuning; the higher max allows large windows on clean high‑latency or high‑bandwidth paths.netdev_max_backlog: Maximum number of packets that can be queued when the kernel receives them faster than it can process; 250 000 is a common safe value on modern hardware.tcp_congestion_control = htcp: Uses HighSpeed TCP Congestion Control, designed for fast long‑fat‑pipe links.default_qdisc = fq: Fair Queuing with pacing, often recommended for servers with modern kernels.
Applying the Configuration
Immediate Application
After saving /etc/sysctl.d/10g.conf, apply the settings to the running kernel:
sudo sysctl --systemThis command reloads all configuration files under /etc/sysctl.d, /run/sysctl.d and /usr/lib/sysctl.d, and applies all settings without requiring a reboot.
Verification
You can verify that the values have been applied by querying a few key parameters:
sysctl net.core.rmem_max
sysctl net.core.wmem_max
sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_rmem
sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_wmem
sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control
sysctl net.core.default_qdiscThe output should reflect the values specified in 10g.conf, confirming that the tuning is active.
Usage and Testing
Once the configuration is applied, you can re‑test SMB/NFS throughput (for example, from your Nextcloud host or other Debian clients) using representative workloads or tools like iperf3, large file copies, or application‑level benchmarks. The tuning primarily benefits sustained transfers where the network path was previously constrained by default TCP buffer limits rather than disk or CPU.
Autoupdate on Debian
sudo apt install unattended-upgrades
sudo dpkg-reconfigure unattended-upgrades
Add a user to the sudoers group on Debian 13
usermod -aG sudo masterAdd E-Mail account to MS Outlook
Introduction
Microsoft 365, Azure or Exchange Server uses a proprietary protocol for E-Mail, Calendar and Contacts/Address Book. It is possible to add multiple E-Mail accounts, either with IMAP, POP3 or M365 to MS Outlook.
Configuration
Goto "Settings" --> Accounts --> Add Account
It looks slightly different on Windows or MacOS
Enter your E-Mail address and click on "continue".
If Outlook does not determine the account type automatically, enter "Microsoft 365".
Follow the instruction on the screen. It will guide you through the log in process. If Outlook ask for the profile type, I recommend "business profile".
You will need your E-Mail address and your password.
Functionality
All functions provided by M365 are supported:
- send E-Mail
- receive E-Mail
- calendar (Appointments)
- addressbook
The addressbook shows only contacts, that you have already contacted. However, you can search the addressbook in the name field by writing three characters of the name of the person you are looking for.
Add M365 account to Apple Mail
Introduction
Microsoft 365, Azure or Exchange Server uses a proprietary protocol for E-Mail, Calendar and Contacts/Address Book. It is possible to add and use E-Mail functionality from Microsoft by adding it to Apple Mail.
Configuration
Open Menu "Mail" --> Settings --> Accounts --> "+"
Select "Micosorft Exchange" --> "Continue"
Enter your E-Mail address. Click on "Sign in".
Click "Sign in".
Follow the instruction on the screen to log in. And finally "Accept" the permissions, that Microsoft requests on your Mac Computer.
Click "Done".
Functionality
All functions provided by M365 are supported:
- send E-Mail
- receive E-Mail
- calendar (Appointments)
- address book
Calendar
To use the Exchange calendar, you have to utilize "Calendar" on MacOS.
The functionality is limited. It will show all the appointments you have. However, it will not show free or reserved time of other people, hence "Calendar" does not access the address book of the M365 Exchange server. If you create a new appointment, you are also not able to invite other people from the M365 tenant. You have to copy the E-Mail addresses from "Apple Mail" to the invitation.
Address book
To use the address book, you have to utilize "Contacts" on MacOS. Select the correct address book (from the Exchange server). In my case it was: Directories --> Exchange Global Address List.
You can search the address book in the name field by writing three characters of the name of the person you are looking for.
MacOS Tips & Tricks
How to Disable SIP
Introduction
System Integrity Protection (SIP)
SIP protects MacOS from cyber attacks. However, it also prevents the installation of certain software. So it can become necessary to disable SIP temporarily.
Boot into recovery mode
Silicon M1, M2, M3
Shut down your Mac and wait for 20 seconds. Then, hold the power button until you see the "Loading startup options" message under the Apple logo. Then, select Options and click Continue to enter the macOS Recovery screen.
Intel based
Restart your Mac and wait for 30 seconds. Press the power button and immediately hold Command + R keys on the keyboard until you see the Apple logo. Your Mac will boot into macOS Recovery after a while.
Open a terminal
Under utilities, you will find "Terminal". Open it.Type the following command:
csrutil disableAfter that reboot the Mac, make all the necessary changes and enable SIP after that by entering the command:
csrutil enable
Boot into recovery mode
Intel based
Reboot and press:
- Command-R:
Start up from the built-in macOS Recovery System. Use this key combination to reinstall the latest macOS that was installed on your system, or to use the other apps in macOS Recovery. - Option-Command-R:
Start up from macOS Recovery over the internet. Use this key combination to reinstall macOS and upgrade to the latest version of macOS that’s compatible with your Mac. - Option-Shift-Command-R:
Start up from macOS Recovery over the internet. Use this key combination to reinstall the version of macOS that came with your Mac or the closest version that’s still available.
Silicon based
- Turn off your Mac.
- Press and hold the Power button.
- A message stating you'll be able to access startup options soon will appear. Keep holding the button down.
- Click Options > Continue to open up Recovery.
Useful Link
MacOS - Flush DNS Cache
Introduction
For some reasons Apple nurses a bug in the DNS resolver. This leads to the problem, that some FQDNs cannot be resolved correctly. The workaround is quite simple.
Resolution
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponderMacOS - Privacy hint / OCSP patch
Introduction
The Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) is an Internet protocol used for obtaining the revocation status of an X.509 digital certificate.It is described in RFC 6960 and is on the Internet standards track. It was created as an alternative to certificate revocation lists (CRL), specifically addressing certain problems associated with using CRLs in a public key infrastructure (PKI). Messages communicated via OCSP are encoded in ASN.1 and are usually communicated over HTTP. The "request/response" nature of these messages leads to OCSP servers being termed OCSP responders.
The OCSP protocol is used to check whether or not a certificate has been revoked. In this context, it is used to give Apple the opportunity to revoke the “blessing” it has given to a specific piece of software. Whenever you start an application, MacOS checks back with the OCSP server.
Resolution
There are two ways to prevent MacOS from checking back to Apple.
Local patch
echo 0.0.0.0 ocsp.apple.com | sudo tee -a /etc/hostsRouter patch
Discussion
In fact, Apple does not associate the information coming with this request to any person or any IP address. Apple does also not track, when you start an application. Apple could figure out, which software vendor an application is coming from (thinking about Microsoft, that leaves a lot of possibilities).
In the end, it is a simple check whether a certificate is valid or not.
Security professional criticized that a man in the middle attack is possible and you might start an application of which the certificate is revoked. The data itself is also transferred over HTTP without encryption. So a 3rd party could get an idea than somebody runs software from a specific software vendor.
Keeping aside the security concerns, it could be a little bit slower to start an application with a low bandwidth internet connection. In that case, it could make sense to block the request.
Useful links
https://www.sentinelone.com/blog/what-happened-to-my-mac-apples-ocsp-apocalypse/
Map a shared drive on MacOS
Introduction
Mapping of network drive seems to be a big issue. Hopefully this manual brings a little light into the fog.
Requirements
Any kind of network resource, that offers any kind of network share. A network resource can be:
- Windows Server
- Linux Server
- NAS (Network attaches storage)
- SMB or SAMBA
- CIFS
- NFS
- (FTP (SFTP))
- AFP (Apple File Protocol)
This manual will focus on SMB
Map a drive with MacOS and Finder
Open Finder and go to this menu or simply press cmd-k
Finder will provide you with a list of network resources it already found:
If you can already see your resource, you can click on it. If not, you will need to input the resource manually. You will need the protocol and ether the IP Address or an DNS name.
Finder understands these protocols:
- smb
- cifs (http, https)
- ftp
- afp
If our resource is located on nas01.simmy.ch and the protocol is smb, you will have to type in:
smb://nas01.simmy.ch
Most resources are protected with username and password:
If you manage to enter your username and password correct, please select the resource, you want to access:
Next thing you will see is the data, that is located on the network share:
Speedup Settings for 10 GbE
Introduction
- SMB signing and encryption enabled by default on macOS, adding CPU and latency overhead to reads.
- Apple SMB extensions (AAPL / fruit) and Finder metadata lookups, which can severely hurt directory reads and some sequential patterns.
- macOS SMB client defaults in /etc/nsmb.conf not optimized for high‑bandwidth, wired 10 GbE connections.
Quick fix
On macOS 15.6.1 (run with sudo ), create or edit /etc/nsmb.conf :
[default]
signing_required=no
mc_on=yes
mc_prefer_wired=yes
protocol_vers_map=6
smb_neg=smb3_only
dir_cache_off=yes
Proxmox Virtual Environment - PVE
PVE - VM does not stop
Introduction
Sometimes a virtual machine cannot be stopped from the GUI.
Resolution
qm stop <number>Useful links
https://bobcares.com/blog/proxmox-cant-stop-vm/
PVE - No quorum error
Introduction
A typical error on a PVE cluster is
No Quorum error
It can happen, when other machines of the cluster stop functioning.
Resolution
pvecm expect 1Useful links
PVE - Can't lock file
Can't lock file
manual SSH:
goto /run/lock/qemu-server
delete lock-xxx.conf
qm unlock xxx
Simple script:
#!/bin/sh
echo
echo '-----AUTHOR: https://dannyda.com-----'
echo
echo '---Existing locks---'
qm unlock $1
ls -l /run/lock/qemu-server
rm -f /run/lock/qemu-server/lock-$1.conf
qm unlock $1
echo
echo '---Remaining locks---'
ls -l /run/lock/qemu-server./killvm.sh xxx Import the voyager Root Certificate into your system
Introduction
To ease the use of servers/services of this domain it is recommended to trust the root certificate of this domain. This text describes how-to import the root certificate and start trust the different serves/services
Vivaldi
The Vivaldi browser is not so straight forward. You have to enter
chrome://settings/certificates
Then it will display the certificate management; goto "Authorities":
"Import" all certificates you need.
Don't forget to trust them.
Brave
Goto to the settings menu of your browser. Usually on the right upper corner.
From the opening menu choose "Settings".
Search for "certificate" or go to Privacy and Security Settings and choose "Manage certificates".
Select ca_simmy.ch.crt
Make sure that under trust settings "Trust this certificate for identifying websites" is enabled. The other options are for future use.
Windows
Import the certificate to your local certificate store.
Dafür "Computerzertifikate verwalten" aufrufen. Beim Punkt "Vertrauenswürdige Stammzertifizierungsstellen" mit der rechten Maustaste klicken: Alle Aufgaben - Importieren
ACHTUNG: Nicht unter "Eigene Zertifikate" speichern, das Zertifikat funktioniert dort nicht!
Danach einfach die Masken jeweils bestätigen. Hier nochmals der Pfad:
Schliesslich auf "Fertig stellen" und freuen, dass die Verbindung nun verschlüsselt ist.
iOS
bei iphone kann ich dir sagen: pack dir das irgendwo per web erreichbar, am besten in deinem LAN, rufe dann die .crt-datei mit -safari- auf und sage dem browser dann, dass er das crt installieren darf. das ist bisher die zuverlässigste variante. alles andere via "apple dateien" oder seafile oder oder funktionieren nicht, da der trigger nicht initiiert wird
Patrick Beck, 23.10.2022
Download certificate
Upper left corner, ca_simmy.crt.
Add custom certificates to Apache
Introduction
In numerous cases you want to enable https on a webserver like Apache. So I decided a once and for all documentation for it.
Configuration
a2enmod ssl
a2enmod rewrite
systemctl restart apache2Edit the Apache configurationf file /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
Add at the end:
<Directory /var/www/html>
AllowOverride All
</Directory>Edit the Apache configuration file for the default website: /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf
<VirtualHost *:443>
# The ServerName directive sets the request scheme, hostname and port that
# the server uses to identify itself. This is used when creating
# redirection URLs. In the context of virtual hosts, the ServerName
# specifies what hostname must appear in the request's Host: header to
# match this virtual host. For the default virtual host (this file) this
# value is not decisive as it is used as a last resort host regardless.
# However, you must set it for any further virtual host explicitly.
#ServerName www.example.com
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
# Available loglevels: trace8, ..., trace1, debug, info, notice, warn,
# error, crit, alert, emerg.
# It is also possible to configure the loglevel for particular
# modules, e.g.
#LogLevel info ssl:warn
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
SSLEngine on
SSLCertificateFile /var/lib/zentyal/conf/ssl/ssl.cert
SSLCertificateKeyFile /var/lib/zentyal/conf/ssl/ssl.key
# For most configuration files from conf-available/, which are
# enabled or disabled at a global level, it is possible to
# include a line for only one particular virtual host. For example the
# following line enables the CGI configuration for this host only
# after it has been globally disabled with "a2disconf".
#Include conf-available/serve-cgi-bin.conf
</VirtualHost>You have to add the lines 22, 23 and 24. I use the same certificate all over the system, so I point to already existing certificates.
Restart the service:
service apache2 restartYou might want to insert this at the beginning of the file:
<VirtualHost *:80>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteRule ^/?(.*) https://%{SERVER_NAME}/$1 [R=301,L]
</virtualhost>Useful links
https://techexpert.tips/apache/enable-https-apache/
Add metager as search engine to your browser
Introduction
MetaGer is a meta-search engine focused on protecting users' privacy. Based in Germany, and hosted as a cooperation between the German NGO 'SUMA-EV - Association for Free Access to Knowledge' and the University of Hannover, the system is built on 24 small-scale web crawlers under MetaGer's own control.
With MetaGer as default searchengine you can instruct your browser to automatically use MetaGer when search queries are entered i.e. into the address bar.
I used to recommend MetaGer as default search engine for the browser. However, it proved to be unreliable. The search result were incomplete.
Features
Search queries are relayed to as many as 50 search engines.The results are filtered, compiled and sorted before being presented to the user. Users can select the search engines to query according to their individual choices among other options (such as "check for availability and sort by date"). Privacy protection is implemented by several features: MetaGer provides access to their services only through encrypted connections. As of December 2013, there is also a TOR Hidden Service (b7cxf4dkdsko6ah2.onion/tor/) that allows users to access the MetaGer search functionality from within the TOR network. Since February 2014 MetaGer additionally offers the option to open the result webpages anonymously ("open anonymously").
Add Metager as search engine
Goto settings --> Search engine --> Add
Enter:
Search engine: Metager
Shortcut: :mt
URL: https://metager.org/?q=%s
Set MetaGer as default search engine
MetaGer Apps
MetaGer App
This App brings the full Metager power to your smartphone. Search the web with one touch while preserving your privacy. There are two ways to get our App: install via the Google Playstore or (better for your privacy) get it directly from our server.
MetaGer Maps App
This App provides a native integration of MetaGer Maps (powered by Openstreetmap) on your mobile Android device.
Therefore, the route planner and the navigation service is running very fast on your smartphone. The app is faster compared against the use in a mobile web browser. And there are some more advantages- check it out!
After the first start you will be asked for the following permissions:
- Access to positioning data => With GPS activated we can provide better search results. With this you get access to the step-by-step navigation. Of course, we don't store any of your data and we don't give any of your data to third persons.
- Access to images, media and files on the device => This permit is necessary for the automated update of the App. If there is a newer version it can be stored in your download archive and will be installed automatically. Without this permission you have to do a manual installation every time there is an update.
Useful links
https://restoreprivacy.com/private-search-engine/
Thunderbird
Installation of Thunderbird
Introduction
Prerequisites
Download the newest Version of Thunderbird directly from their Webpage.
Installation
Installation on MacOS
Just click on the downloaded .dmg file and copy it to your programs directory.
Installation on Fedora
tar -xvjf thunderbird-128.3.0esr.tar.bz2
Add Microsoft Outlook Account/Teams to Thunderbird
Introduction
Microsoft 365, Azure or Exchange Server uses a proprietary protocol for E-Mail, Calendar and Contacts/Address Book. It is possible to connect to a Microsoft E-Mail account with Thunderbird. It is also possible to connect to more than one account. Especially if it comes to Teams, which can be used inside of Thunderbird, this feature becomes very useful.
Configuration
Goto account setting and "Add Mail Account".
You will need your E-Mail address and your password.
After clicking continue, you will be asked to enter your password again. No matter what happens next, you will return to Thunderbird.
Select "Exchange/Office365" and click on "Done".
If you are asked to install "OWL", please do it.
Hint
You are now able to use E-Mail and Calendar functionality. So far Contacts/Address book are not working.
Teams:
On the left side you should find the Teams icon. Hover gently over it. It will then show all connected Microsoft Accounts. If you click on one of those account, a new tab will open for teams. Repeat until you opened all the Teams for your tenants.
CSA Webflow
Webflow User Guide
1. Logging In and Dashboard
visit webflow.com/login
Enter username and password.
Enter your TOTP Token.
2. Page Settings
3. Designer
3.1 Design Options
3.2 Components
3.3 Variables
3.4 Style Selectors
3.5 Images
4. CMS Functions
4.1 Collections
4.2 Creating and Editing Items
4.3 Text Formatting
4.4 Image Upload
5. Multilingual Support
6. Video Integration
7. Customizing Fields
8. Publishing
9. SEO and Social Media Optimization
9.1 SEO Settings
9.2 Open Graph Settings
9.3 Testing
Tips and Tricks
Manual installation of WinBox
WinBox
Winbox is a very useful application from mikrotik for the purpose to manage their devices. It is currently in beta stage, so this installation guide might be subject of change.
Download the application from Mikrotik download page. Extract the package to ~/bin. Copy the icon file from the assets/img directory to ~/icons.
ln -s /home/hschindler/bin/WinBox_Linux/WinBox /home/hschindler/bin/winboxCreate the launcher:
Vivaldi - HSTS problem
Docker Tips & Tricks
Name resolution
Introduction
DNS sucks in docker. However, there are two fixes.
Fix no. 1
Create /etc/docker/daemon.json:
{
"dns": ["192.168.1.2", "192.168.1.25"]
}sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker
sudo docker run --rm alpine sh -c "cat /etc/resolv.conf && nslookup hfile.simmy.org"Fix no. 2
Edit etc/default/docker
# Here in Debian, this file is sourced by:
# - /etc/init.d/docker (sysvinit)
# - /etc/init/docker (upstart)
# - systemd's docker.service
# Use of this file for configuring your Docker daemon is discouraged.
# The recommended alternative is "/etc/docker/daemon.json", as described in:
# https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/dockerd/#daemon-configuration-file
# If that does not suit your needs, try a systemd drop-in file, as described in:
# https://docs.docker.com/config/daemon/systemd/
# Docker Upstart and SysVinit configuration file
#
# THIS FILE DOES NOT APPLY TO SYSTEMD
#
# Please see the documentation for "systemd drop-ins":
# https://docs.docker.com/engine/admin/systemd/
#
# Customize location of Docker binary (especially for development testing).
#DOCKERD="/usr/local/bin/dockerd"
# Use DOCKER_OPTS to modify the daemon startup options.
DOCKER_OPTS="--dns=192.168.1.2 --dns 192.168.1.25"
# If you need Docker to use an HTTP proxy, it can also be specified here.
#export http_proxy="http://127.0.0.1:3128/"
# This is also a handy place to tweak where Docker's temporary files go.
#export DOCKER_TMPDIR="/mnt/bigdrive/docker-tmp"DOCKER_OPTS="--dns=192.168.1.2 --dns 192.168.1.25"
It's mandatory to keep this DNS configuration up to date. Otherwise NPM will not be able to resolve internal addresses.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker
sudo docker run --rm alpine sh -c "cat /etc/resolv.conf && nslookup hfile.simmy.org"