Install xrdp on Fedora Xfce
Overview
This document describes how to install and configure the XRDP server on Fedora 43 with the Xfce desktop environment so that Windows, macOS, and Guacamole clients can connect via RDP. Each Linux user who should be able to log in via XRDP needs their own startwm.sh to launch Xfce correctly.
Prerequisites
- Fedora 43 VM or physical host with the Xfce desktop environment installed (PRETTY_NAME="Fedora Linux 43 (Xfce)"). [web:14]
- Root or sudo access on the Fedora system.
- Network connectivity from RDP clients (Windows, macOS, Guacamole) to TCP port 3389 on the Fedora host.
Install and Enable XRDP
Install XRDP and its Xorg backend, then enable and start the service. Fedora 40/41 XRDP documentation uses the same pattern and works on Fedora 43. [web:21][web:17]
sudo dnf install -y xrdp xorgxrdp
sudo systemctl enable --now xrdp
sudo systemctl status xrdpOpen the Firewall for RDP
If firewalld is running, open TCP port 3389 permanently and reload the firewall rules. [web:21][web:17]
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3389/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadCreate startwm.sh for Each User
On Fedora, XRDP uses a per-user startup script named startwm.sh in the user's home directory to start the desktop session. Fedora's XRDP guide shows this pattern for multiple desktops; for Xfce the command is dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/startxfce4.
Repeat the following steps for each user account that should be able to log in via XRDP:
# as the target user (not root)
cat > ~/startwm.sh << 'EOF'
#!/bin/sh
export LANG=en_US.UTF-8
export LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8
exec dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/startxfce4
EOF
chmod 755 ~/startwm.sh
Explanation:
dbus-launch --exit-with-sessionensures a proper D-Bus session is created for Xfce, which is required for a fully functional desktop over XRDP./usr/bin/startxfce4starts the Xfce session.chmod 755makes the script executable so XRDP can run it at login.
Optional: Global /etc/xrdp/startwm.sh
If you want a single configuration for all users, you can copy the same script to /etc/xrdp/startwm.sh so XRDP uses it globally. This approach is also referenced in XRDP discussions about custom session commands.
sudo cp /home/<username>/startwm.sh /etc/xrdp/startwm.sh
sudo chmod 755 /etc/xrdp/startwm.sh
sudo systemctl restart xrdp
Replace <username> with a real user name when copying from an existing script.
SELinux Considerations (Optional)
On some Fedora installations, SELinux can interfere with XRDP. Recent XRDP-on-Fedora guides use chcon to assign the bin_t type to XRDP binaries if SELinux denials occur. [web:17]
sudo chcon --type=bin_t /usr/sbin/xrdp
sudo chcon --type=bin_t /usr/sbin/xrdp-sesman
sudo systemctl restart xrdpTesting with a Native RDP Client
Test XRDP with a standard RDP client before integrating with Guacamole. Fedora XRDP documentation uses Windows Remote Desktop as the reference client. [web:21]
- From a Windows machine, open Remote Desktop Connection (
mstsc.exe). - Enter the Fedora host name or IP (for example
fedora-xfce.example.local) and connect. [web:21] - Log in using a Fedora user that has a
~/startwm.shconfigured. - Verify that an Xfce desktop session appears and is usable.
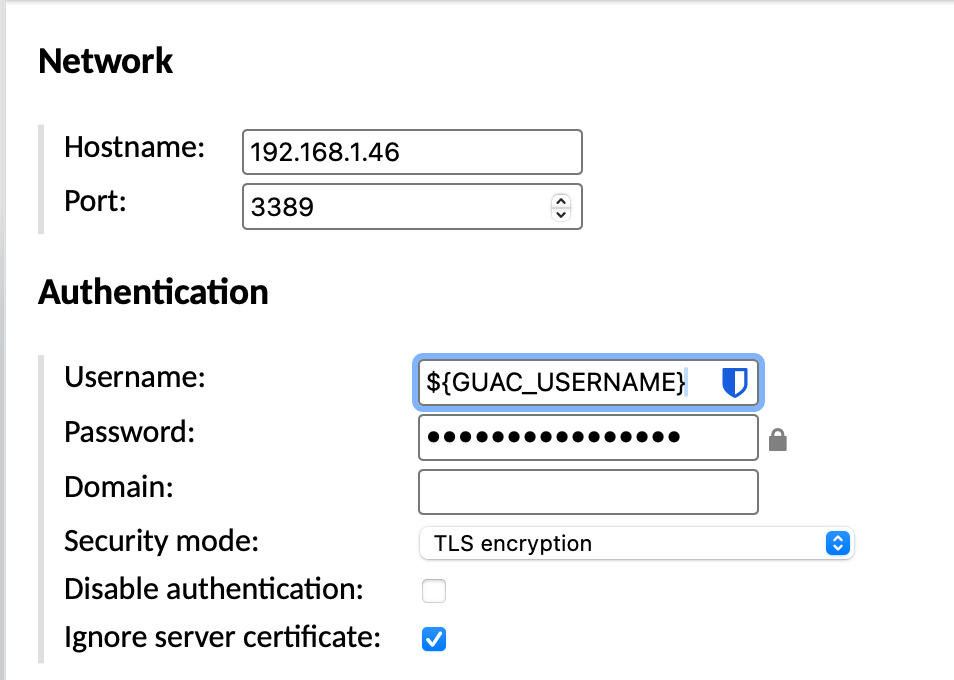
Using XRDP from Guacamole
Once XRDP and Xfce are working locally, Guacamole can connect using the RDP protocol. The key is to match the security mode and certificate options so that negotiation succeeds.
| Setting | Value |
| Protocol | RDP |
| Hostname | IP Address |
| Port | 3389 |
| Username | $(GUAC_USERNAME) |
| Password | $(GUAC_PASSWORD) |
| Security Mode | TLS |
| Ignore server certificate | enable |
Summary
- Install XRDP and Xorg backend with
dnf install -y xrdp xorgxrdp, then enable the service. - Open the firewall for TCP port 3389 if
firewalldis running. - Create a per-user
~/startwm.shcontainingdbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/startxfce4and make it executable. - Optionally, place the same script at
/etc/xrdp/startwm.shfor a global configuration. - Verify RDP access with a native client (e.g., Windows mstsc), then configure an RDP connection in Guacamole pointing at the Fedora 43 XRDP server.